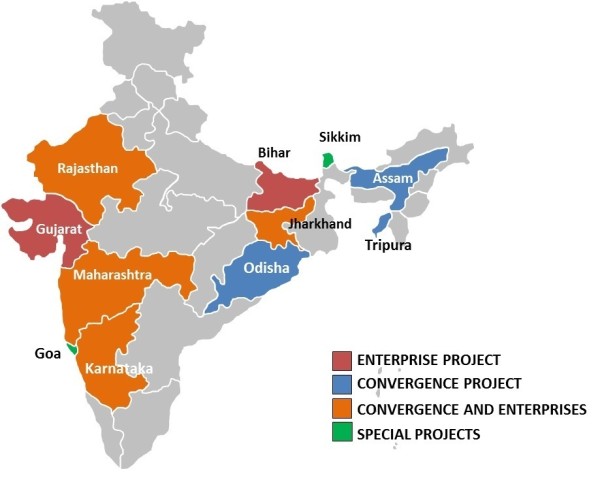
Map of Kudumbashree-NRO’s partner-States (as of January 2017)
In 2012, Ministry of Rural Development, Government of India recognized Kudumbashree’s potential to support other States by anointing it as a National Resource Organisation (NRO) under the National Rural Livelihood Mission (NRLM). As a NRO, Kudumbashree holds the mandate to partner with interested State Rural Livelihood Missions (SRLMs) and provide them with technical and implementation support.
The NRO became functional from May 2013 onwards. It is an integral part of Kudumbashree Mission.
Since 2013, KS-NRO has developed long-term partnerships with 11 States, namely Assam, Bihar, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Odisha, Gujarat, Goa, Sikkim, Tripura and Rajasthan. KS-NRO has special short-period projects in 2 States, namely Sikkim and Goa. Foreign countries such as Ethiopia and South Africa have also demonstrated interest in taking the support of KS-NRO in adapting Kudumbashree’s model in their respective countries.

KS-NRO believes that each location requires interventions suited to its particular context. Hence, KS-NRO draws from the experience of Kudumbashree, and works with its partner-SRLMs to customize activities for implementation in their States.
Creating local capabilities for consolidation and expansion to new areasKS-NRO focusses on building local resource pools in the partner-States. This strategy based on the understanding that locals are better positioned to work for their community. A strong community cadre is expected to ensure the sustainability and expansion of project activities in the aftermath of the pilot period.
Mentoring by experienced persons from the community in KeralaKS-NRO selects and assigns resource persons with experience of working with Kudumbashree in Kerala as Mentors in partner-States. The Mentors provide day-to-day handholding support to local communities and partner-SRLMs for the implementation of the project.
Professional support for developing systems for monitoring, training and hand-holdingKS-NRO has a team of professionals who provide back-end support to the work done by Mentors and the local resource persons in the partner-States. These professionals, drawn from reputed educational institutions from across India develop monitoring, training and handholding systems for the projects KS-NRO supports in partner-States.
| No. of Partner-States | 11 |
| No. of Programme Managers | 2 |
| No. of Thematic Anchors | 5 |
| No. of Field Coordinators | 14 |
| No. of Young Professionals | 1 |
| No. of Administrative Staff | 5 |
| No. of Mentors | 116 |
The PRI-CBO Convergence approach is based on the premise that if institutions of the poor such as Community Based Organisations (CBO) and Panchayati Raj Institutions (PRI) collaborate with each other to work for the development of the village, they can significantly enhance the livelihood and social security of the vulnerable and poor.It is based on Kerala’s experience of NHG-ADS-CDS working closely with the Gram Panchayats (GPs). The pilots implemented in various states have helped develop a ‘Proof of Concept’ for universal implementation of this programme under NRLM.
The PRI-CBO Convergence project capacitates PRI representatives and SHG members in addition to creating platforms for their convergence. The PRI and CBO are expected to work together to strengthen the poor’s access to entitlements and enhance the public’s participation in local governance. To achieve these goals, a cadre of motivated community individuals called Local Resource Group (LRG) are nurtured in partner-States. The LRG are expected to work towards enabling the convergence of PRI and CBO for the development of the village. As part of the project strategy, the CBOs and PRI are introduced to participatory assessment, planning and monitoring tools to help local communities build awareness and plan for their access to schemes and benefits.
The project was initially piloted in 5 states of Assam, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Odisha and MoU in these states expired in 2017. Some of the achievements in these states include:
| Status of Activities and Outcomes in Pilot Project where MoU Expired in 2017 | |||||||
| Name of State | Number of Active LRGs | Number of Internal Mentors | Number of VOCC formed | Number of GPCC formed | % of SHGs completed PAE | % of SHGs completed EAP | % of SHGs completed GP2RP |
| Assam | 209 | 30 | 36 | 35 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Jharkhand | 221 | 59 | - | 27 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Karnataka | 173 | - | - | 31 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| Maharashtra | 170 | 107 | 58 | 58 | 95.41 | 100 | 100 |
| Odisha | 109 | 25 | - | 7 | 88.63 | 100 | 91.67 |
Project locations
Since 2013, the PRI-CBO Convergence project has been piloted in partner States such as Maharashtra, Odisha, Jharkhand, Rajasthan, Karnataka and Assam. In 2016, MoU was signed between Tripura and Kudumbashree for the implementation of PRI-CBO Convergence project in pilot locations in Tripura.MoU with the state of Chhattisgarh is in the process of finalization. Based on the experience of the pilot project, Assam, Jharkhand and Odisha have planned to scale up the project in the respective states.
| Number of Partner States | 6 |
| Number of Districts | 27 |
| Number of Blocks | 57 |
| Number of Gram Panchayats/ Village Committees | 460 |
| Number of Mentors | 50 |
Tools for Participatory Planning and Poverty Reduction
KS-NRO has developed the following tools that are used by SHG households in pilot locations for understanding and documenting gaps in entitlement access, planning for its access and undertaking joint action with Gram Panchayats for eradicating poverty at the village level.
Participatory Assessment of Entitlements (PAE):PAE is a SHG-level ribbon-exercise to help generate awareness about schemes/benefits and identify left-out families.
Entitlement Access Plan (EAP):EAP is a target plan prepared by each village organisation (VO) to address gaps in the access to entitlements identified during PAE.
Gram Panchayat Poverty Reduction Plan (GP2RP): GP2RP is a comprehensive demand plan prepared by SHGs and their federations in partnership with the Gram Panchayats for local development.
Project Sustainability Indicators
The PRI-CBO Convergence project is designed such that each partner-State eventually takes over the implementation of the project from Kudumbashree-NRO.
Kudumbashree-NRO aims to facilitate a self-sustainable and smooth transition of the PRI-CBO Convergence project by focusing on aspects such as:
MEC Project
Micro Enterprise Consultants as a concept started by Kudumbashree in Kerala in the year 2004. Based on the experiences of Kudumbashree, KS-NRO piloted the MEC Project in 6 states, namely Bihar, Gujarat, Jharkhand, Karnataka, Maharashtra and Rajasthan for micro-enterprise development through building and strengthening local pool of Micro-enterprise Consultants (MEC) in partner-States.
Micro Enterprise Consultants (MECs) are drawn from the community, trained and placed locally to provide handholding support to existing and potential entrepreneurs on a chargeable basis. The MECs work in groups which are registered partnership firms offering business consulting services, leveraging the different skill sets of its members in the interest of providing quality services to targeted clients.
Prime activities in partner states include:
• Identifying and selection of MEC
• Capacitation of MEC and placement of MEC Groups
• Establishing MEC – CBO linkages for sustainable rural enterprise development
• Roll out of measurable and effective monitoring mechanisms
39 personnel drawn from Kudumbashree’s resource pool of former CDS Chairpersons, Micro- Enterprise Consultants, KAASS members provide on-ground mentoring and hand-holding support for project activities in partner-States.Young Professionals are engaged in supporting mentors, designing and developing training, planning and monitoring modules and tools.
The MEC Project pilots are taken up by the State Rural Livelihood Missions (SRLM) as part of their Annual Action Plans for (National Rural Livelihood Mission) NRLM. Kudumbashree-NRO provides technical support in design and implementation. The interventions are locally contextualized jointly by the SRLM and KS-NRO.
The specific roles of the SRLM are:
• Mission Management Units at State, District and Block level takes ownership of the project activities and provides support and guidance throughout
• Helps establish relationship with existing community cadre and field level stakeholders for smooth running of project
• Conducts regular monitoring and review of the work of the MEC groups and their relationship with the community institutions
• Interfaces with banks and other sources of financial support
• Plans for replication and scaling-up of the pilots to other parts of the State
The States and SRLMs implementing the MEC Project are Jeevika - Bihar Rural Livelihoods Promotion Society, GLPC - Gujarat Livelihood Promotion Company, JSLPS - Jharkhand State Livelihood Promotion Society, Sanjeevini - Karnataka State Rural Livelihood Promotion Society, Umed - Maharashtra State Rural Livelihoods Mission and Rajeevika - Rajasthan Grameen Aajeevika Vikas Parishad(under Rajasthan Rural Livelihoods Project).
Coverage Map of MEC Project
4 Pillars of the MEC Project
Stakeholders involved
Capacity Building of MECs
The Capacity Building of the selected MECs forms a crucial period in the implementation of MEC project in partner states. Capacity Building modules and activities are divided as per the content designed for each:
1.Training in Entrepreneurship Development (TED)
2.Certificate in Rural Enterprise Administration and Management (CREAM)
3.Training in Rural Enterprise Administration and Management (TEAM)
4.Market and demand assessment exercises for hands-on practice of concepts
5.Exposure Visits for ‘seeing and learning’
Stages of Enterprise promotion and services offered by MEC
Stages Services offered by MEC
Opportunity identification for entrepreneurs Facilitation of orientation on business opportunities in the local area
Entrepreneur orientation and training Module creation and training facilitation
Business planning Conducting Viability check and Preparation of business plan
Credit linkages Providing linkages for credit from banks and Community institutions
Enterprise setting-up and market linkages Providing market support for purchase of raw materials and selling of finished products
Performance tracking and advisory Generating PTS sheet and financial statements in a periodic manner and providing consultancy based on the data captured
Growth diagnostics and problem solving Identifying issues in an existing enterprise and finding out solutions to increase its profitability
Performance Tracking System for the micro enterprises
Performance Tracking System (PTS) is a method of systematic collection and analysis of business information, to understand and measure business performance
It involves:
• Micro-Enterprise Consultants (MEC) ensuring that the entrepreneur maintain basic records for the business
• MEC collecting the transaction information from the records of the business, and generating financial statements
• The financial statements allowing for comparison with:
– Same enterprise over a period of time
– Similar businesses in the same marketplace
Components of PTS
• Enterprise Registration: It captures the basic information of an enterprise at the onset of MEC intervention
• Maintenance of Business records: MECs train the entrepreneur to maintain daily record of transactions
• Intermediary Calculations: MEC consolidates the daily records kept by the entrepreneur to generate a PTS Sheet
• Financial Statements as Outputs: MEC uses the information from business records to compute Cash Flow statement, Profit and Loss statement and Balance Sheet of the enterprise
• Comparative Analysis: Using financial statements, the MEC compares the performance of the enterprise over time and with other enterprises in the same time period
• Advisory Services: Based on the analysis, MEC offers advice to the entrepreneur for improving business performance
Mobile App for PTS
PTS Mobile application to be used by all MECs on smartphones
Project Accomplishments
• Master trainers pool from partner states have been created to facilitatecapacity building of MECs
- By partner states as part of scale up activity
- By KS-NRO while implementing Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Program (SVEP) in partner states.
• Internal mentors have been created in partner states for scale up activities
• SVEP design has been substantially based on the experiences of MEC Project pilots undertaken by KS-NRO
• KS-NRO has developedcapacity building training syllabus in business skills, pedagogy and materials for SVEP
• First-of-its-kind Micro Enterprise accounting and near- (Enterprise Resource Planning) ERP application has been initiated through introduction of Performance Tracking System (PTS) and its Mobile App
The successful demonstration of proof of concept in pilot locations of KS-NRO’s MEC project contributed to the universalization of the concept of Micro-Enterprise Consultants in India in the form of Government of India’s Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme. Kudumbashree-NRO is accredited as one of the NROs to provide support in the implementation of SVEP to interested States.
Under SVEP, a pool of block level community cadre – Community Resource Person for Enterprise Promotion (CRP-EP) - will be trained in business management to support the rural poor to set up their enterprises and handhold them in the initial six months of start-up. SVEP entails building the capacity of NRLM and SHG federations to monitor the work of CRP-EPs. It also has provisions for the use of integrated ICT techniques and tools for training and capacity building, enterprise advisory services and to provide loans to rural entrepreneurs from the NRLM SHGs and federations and the banking system including the MUDRA bank.
SVEP intends to fill in the gaps of a missing knowledge ecosystem (exposure to new ideas, soft skills for triggering, lack of domain skills, etc.), a missing incubation system (personalized advisory, feasibility intelligence, common startup pitfalls, etc.) and a missing finance eco-system (customized need based finance, financial linkage, on-going handholding), to address the obstacles faced by first generation entrepreneurs.
NRLM Resource / Intensive Block will be the unit of implementation for SVEP. Under SVEP a Block Resource Centre for Entrepreneurship Promotion (BRC-EP) will be setup to occupy the trained CRP-EP. There is a provision for Community Enterprise Fund (CEF) for supporting enterprises.
Special Projects: KS-NRO Support for Institution Building
KS-NRO provides technical support to partner-States for short term special projects based on their needs. These special projects are customized to meet the requirements of the partner-States based on NRLM. Currently, KS-NRO is in partnership with Sikkim and Goa for the implementation of short-term special projects in pilot locations.
With its partnership with Sikkim and Goa, the objective is of creating a model for supporting both PRI and CBO Networks and well as for developing a community based system for supporting micro enterprises for effective convergence leading to sustainable and better implementation of NRLM. In the long run the partnership is expected to result in the creation of a robust institutional structure of the poor that is closely linked to local governance and development. Towards achieving this, the partnership involves:
Institution Building and Developing federations for the existing Self Help Group as part of the strategy
Support the community in its micro planning activities
Undertaking strategy formulation for better implementation of the programme aimed at community mobilisation, institution building, Convergence and Livelihood generation
Developing trained community cadre for addressing poverty by enhancing and capacitating human resource in villages for both PRI based convergence and micro enterprise development.
Enabling Panchayati Raj Institution’s convergence with Community Based Organizations for livelihood and service delivery through different centrally Sponsored/State sponsored schemes
Providing organizational, and functional capacity building to both PRI & CBO leaders and members
Strengthening CBO (SHG and its federations) to engage with PRIs for addressing the special needs of the poor and the marginalised.
Developing and executing community based sensitization campaigns
Strengthening of production & marketing strategy for improving the livelihood sector
Create systems in place for sustainability.
Project Footprint
No. of States-2
No. of Districts-4
No. of Blocks-12
No. of GPs-132
No. of Mentors-6